Learn more about Gum Disease Treatment: Causes , Treatment & Prevention
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is a mild type of periodontal disease. It causes gums to become red, swollen, and easily bleed. At this point, there is typically little to no discomfort.
What is periodontitis?
If gingivitis is left untreated the infection progresses next stage called periodontitis. As time progresses, the plaque on the surface of the tooth will spread and grow below the gum line. The toxin produced by the bacteria in the plaque irritates the gums. Toxin induces a persistent inflammatory reaction in which the body attacks itself, and the supporting tissues and bone are destructed. Gums detach from teeth, forming pockets (spaces between teeth and gums) that are infected. As the disease progresses, pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are lost. This destructive mechanism also has very mild symptoms. Eventually, the teeth can become loose and need to be removed.
What is a gingival pocket?
The gingival pocket is a gap formed between the tooth and the gum, which causes the gum to swell leading to gum disease. The development of these pockets is due, to the deposition of plaque at the gum line and progressing under the gum.
Who is a periodontist?
A dentist who specializes in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periodontal disease and the insertion of dental implants is a periodontist. Periodontists are also specialists in the diagnosis of oral inflammation. Periodontists undergo rigorous training in these fields, including three additional years of training after dental school.
What is the distinction between gingivitis and periodontitis?
Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease that commonly precedes periodontal disease, an advanced form of gum disease. Gingivitis is frequently treated by seeing your dentist for frequent dental cleanings and brushing and flossing your teeth regularly. On the other hand, periodontitis can lead you to lose your adult teeth and even cause facial deformity if you do not receive regular dental care.
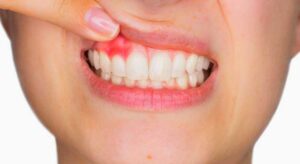
What are the types of gum disease treatments?
The types of gum treatments are non-surgical treatments, surgical treatments, and laser treatments.
• Non-surgical treatments are scaling, root planing, and antibiotic delivery
• Surgical treatments are gum graft surgery, gingivectomy, dental crown lengthening, and osseous surgery.
• Laser treatments are the surgical gum disease treatments done with laser
• Non-surgical treatments are scaling, root planing, and antibiotic delivery
• Surgical treatments are gum graft surgery, gingivectomy, dental crown lengthening, and osseous surgery.
• Laser treatments are the surgical gum disease treatments done with laser
How can my bad breath be treated?
To treat bad breath, it is important to identify the cause. However, there are some remedies to alleviate bad breath. The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends the following measures –
• Brush and floss your teeth daily. Remember to clean your tongue, too, to remove bacteria from your surface.
• Get regular dental check-ups and ensure that dentures or braces are correctly fitted and cleaned (and clean dentures thoroughly every night).
• Stop smoking or chewing tobacco.
• Chewing sugarless gum and sugar-free sweets will also prevent the mouth from drying out.
• Keep your mouth moist by drinking water and chewing sugarless gum or sugar-free hard candy to promote the production of saliva. Eat a diet of foods that need to be chewed thoroughly to keep saliva flowing. Foods that need a lot of chewings, such as apples or carrots, are good choices.
• Over-the-counter mouthwash may help kill bad breath causing bacteria and may temporarily mask bad breathing odors but may not treat the underlying cause.
•Drinking water will hydrate you and moisten your mouth too.
• Brush and floss your teeth daily. Remember to clean your tongue, too, to remove bacteria from your surface.
• Get regular dental check-ups and ensure that dentures or braces are correctly fitted and cleaned (and clean dentures thoroughly every night).
• Stop smoking or chewing tobacco.
• Chewing sugarless gum and sugar-free sweets will also prevent the mouth from drying out.
• Keep your mouth moist by drinking water and chewing sugarless gum or sugar-free hard candy to promote the production of saliva. Eat a diet of foods that need to be chewed thoroughly to keep saliva flowing. Foods that need a lot of chewings, such as apples or carrots, are good choices.
• Over-the-counter mouthwash may help kill bad breath causing bacteria and may temporarily mask bad breathing odors but may not treat the underlying cause.
•Drinking water will hydrate you and moisten your mouth too.
Will gum disease go away on its own?
Periodontal disease is reversible, but only in its early stages. Once your dentist eliminates dental plaque at this stage, you may quickly recover your gum health — but you must also brush and floss regularly to keep it at away. Gum disease will not go away entirely after it has progressed to a severe stage, but it can be treated with suitable dental procedures. It's because advanced periodontal disease causes the loss of support structures around your teeth, like bone. This can be irreversible, but you may be able to rectify it with corrective surgery.
How Can a Periodontist Cure Gum Disease?
Your periodontist will initially educate you on proper oral hygiene. In cases of mild gingivitis, boosting your oral hygiene can reverse the condition and enhance the health of your gums. If the illness has progressed to periodontitis, therapies may include scaling and root planing, laser treatment, and different surgical procedures. Dr. Adatrow will discuss the best choices for your gums with you.


